The long wait for CMMC is ending. The final rule signals a new era of accountability in DoD cybersecurity—contractors who have prepared will have the advantage. As of August 25, 2025, OIRA cleared the final CMMC DFARS rule (217.207, 252), marking a major milestone in rolling out cybersecurity requirements for all DoD contractors and subcontractors. Once the 48 CFR is recorded in the registry and goes live, the DoD will have the ability to require CMMC for all solicitations. There is to be a phased rollout, however all signs point to this becoming more of a suggestion and the reality is CMMC will most likely hit the ground running, FAST!
CMMC 2.0 Structure: CMMC 2.0 has three maturity levels:
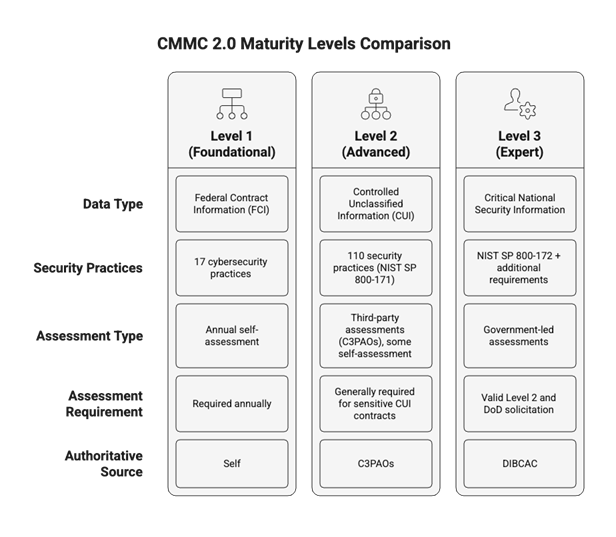
- Level 1 (Foundational): Basic safeguarding requirements for Federal Contract Information (FCI), with 17 cybersecurity practices. Annual self-assessment is required.
- Level 2 (Advanced): Alignment with NIST SP 800-171, Rev 2, requiring 110 security practices to protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Third-party assessments (C3PAOs) are generally required for contracts involving sensitive CUI. Some selected Level 2 programs will be eligible for self-assessment.
- Level 3 (Expert): Incorporates additional requirements from NIST SP 800-172, targeting critical national security programs. Government-led assessments are required.
Assessment Processes:
- Level 1 allows for annual self-assessment.
- Level 2 generally requires third-party assessments by C3PAOs for contracts involving CUI.
- Level 3 requires a valid level 2 from a C3PAO and an active DoD solicitation requiring a level 3. DIBCAC is the only authoritative source of obtaining a CMMC Level 3.
Flexibility
CMMC 2.0 allows companies to use Plans of Action and Milestones (POA&Ms) for noncompliance areas with non-critical controls temporarily. This provides companies with a short-term conditional CMMC level (180 days) ATO while correcting the non-critical controls before being awarded a CMMC Final certification.
Actionable Insights (based on the size of the business)
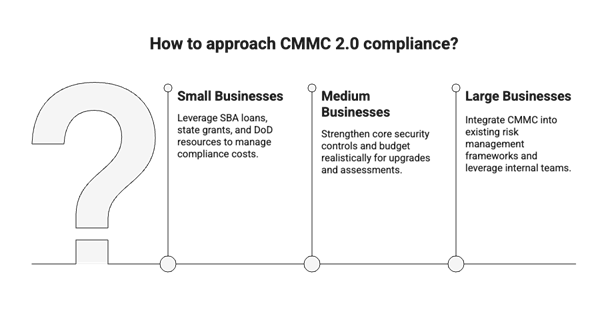
- Small Businesses: For these small businesses, it is important for them to recognize that third-party assessments, upgrading systems, and employee training can be resource intensive. The DoD is exploring support initiatives to help with compliance costs. These small businesses may be able to leverage SBA cyber loans, state grants, and DoD Mentor-Protégé resources to navigate these compliance obligations.
- Medium Businesses: Medium businesses likely have some core security controls already implemented due to other compliance obligations. Allocate resources wisely, budgeting realistically for technology upgrades, consulting help, assessments, and internal manpower. Start with strengthening core security controls and defining your CMMC scope by mapping all the systems, assets, personnel, and processes handling sensitive information. NIST 800-171 is documentation heavy. Most businesses underestimate the required lift around this area.
- Large Businesses: Large businesses likely already have dedicated GRC teams focusing on other relevant frameworks. Integrate CMMC 2.0 into existing enterprise risk management frameworks and leverage internal cybersecurity teams and resources. CMMC involves resources from IT, legal, HR, and finance teams, so ensure those resources are leveled appropriately.
CMMC Checklist
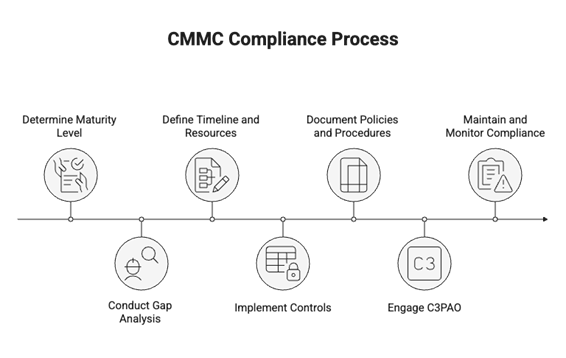
- Determine the required CMMC Maturity Level (as determined by the contract clauses for programs that you are involved in).
- Conduct a Gap analysis using a qualified CMMC Advisor that informs you on areas of prioritization and investments.
- Define a strategic timeline and resources for CMMC Certification
- Implement necessary controls
- Document Policies and Procedures
- Engage a C3PAO for assessments (Mocks recommended, Level 2 required)
- Maintain and Monitor Compliance.
For ALL: Don’t Wait. Preparing for and achieving CMMC certification can take anywhere from 6 to 18 months, depending on your starting point. Waiting is not a strategy.
By taking proactive steps to prepare for CMMC 2.0, defense contractors can ensure they meet the necessary requirements, maintain their eligibility for DoD contracts, and contribute to a more secure and resilient defense industrial base.
For more information, visit the Fortreum website or follow the company on LinkedIn at LinkedIn.com/company/fortreum.
Should you have questions about your FedRAMP, XRAMP, cloud and cybersecurity readiness, please reach out to us at Info@fortreum.com or Contact Us at https://fortreum.com/contact/









